How to measure 3-phase current? Via a multimeter and a clamp meter. For electrical systems to operate smoothly, efficient power distribution is crucial, and 3-phase power systems are popular due to their ability to deliver higher power with balanced loads.
If you want to know about testing single phase with multimeter, I've written complete blog on it!
Maintaining system stability, diagnosing issues, and optimizing energy usage require accurate measurement of 3-phase current.
Why Accurate Measurement Matters?
In a 3-phase power system, accurate current measurement is crucial for several reasons:
- System Performance: Imbalanced currents can lead to uneven power distribution and affect the performance of connected devices. Accurate measurement helps identify any disparities.
- Troubleshooting: Anomalies in current levels can indicate faults, such as overloads or faulty connections. Precise measurements aid in diagnosing and resolving these issues promptly.
- Energy Management: Understanding current consumption patterns enables better energy management, leading to cost savings and efficient resource allocation.
- Safety: Incorrect current measurements can jeopardize the safety of equipment, personnel, and the overall power system. Accurate measurements mitigate potential risks.
Read more about How to Troubleshoot Circuit Board
Basics and Preparations
Multimeters are versatile electrical measurement devices that combine various functions in a single tool. For diagnosing electrical problems, they can measure voltage, current, and resistance. There are two main types of multimeters: analog and digital.
A clamp meter, also known as a current clamp or amp clamp, is a specialized tool used to measure current without breaking the circuit. By clamping the jaws around a conductor, you can measure current non-invasively. When working with live circuits, this is particularly useful.
Preparation: Safety and Tool Checklist
Safety Measures for Live Circuits
The safety of electrical systems, particularly when measuring three-phase current, must be prioritized. Follow these safety guidelines:
- When possible, turn off the circuit you're working on. Use personal protective equipment (PPE) if it's not feasible.
- Ensure your multimeter or clamp meter is in good condition and properly calibrated.
- It is best if you isolate the circuit that you are measuring from other circuits in order to avoid interference.
Tools and Equipment for Accurate Measurement
To perform accurate 3-phase current measurements, gather the following tools and equipment:

- Digital Multimeter
- True RMS Clamp Meter
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Phase Identification Guide
Read More about: Best Multimeter for Electrical Work
How To Measure 3-Phase Current with Multimeter?
How to measure 3-phase current? You can only measure current up to 10A or in some multimeters upto 20 amperes. If the current exceeds it might damage your multimeter or cause serious injury.
Using Multimeter: Step-by-Step
It's now time to take a practical look at measuring 3-phase current with a digital multimeter. Follow these steps to accurately measure the current flowing through each phase.
Step 1: Phase Identification and Setup
Start by identifying the three phases of the circuit - R (Red), Y (Yellow), and B (Blue). Keep track of these phases in the correct sequence to maintain accuracy.

Ensure that the AC current measurement mode is selected in your digital multimeter. Depending on how you estimate the current level, choose a suitable range. As a rule of thumb, start with a higher range and adjust as needed if you are uncertain.
Step 2: Current Measurement and Range Selection
Circuit Connection: Ensure the circuit is powered and active. Then, carefully open the circuit at a point where you intend to measure the current.
Connect in Series:
Make sure the red probe of the multimeter is inserted into the (A) jack, while the black probe is inserted into the (COM) jack. It is essential for current measurements to have this configuration. Attach the red probe to one side and the black probe to the other side of the circuit. By doing so, the multimeter effectively becomes a component of the load.
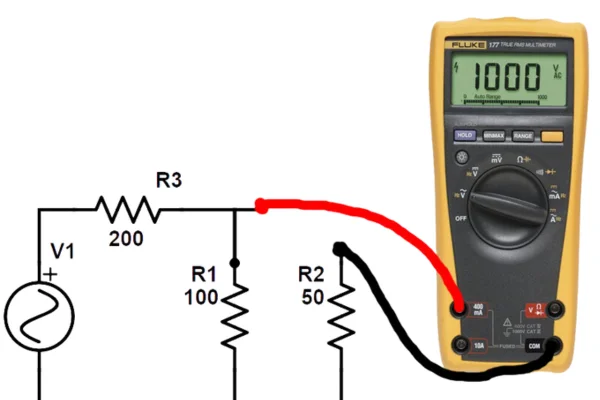
Reading the Current: As the current flows through the multimeter, it will display the current reading on the screen. Note down the readings for each phase - R, Y, and B.
Step 3: Interpreting Results
Balanced System: In a balanced 3-phase system, the readings for each phase should ideally be the same. This indicates a uniform distribution of current.
Unbalanced System: If the readings significantly differ, it suggests an unbalanced load or issues within the circuit.
Read More about: Best Budget Clamp meters
Step 4: Tips and Considerations
Make sure your multimeter is calibrated properly so that you can get accurate readings. Make sure the information is confirmed by a known source. Multimeters display RMS (Root Mean Square) values, which represent effective current. This value takes into account the waveform's heating effect.
How to Measure 3-Phase Current with Clamp Meter?

Using Clamp Meter: Step-by-Step
So, how to measure 3-phase current? Using a clamp meter to measure 3-phase current is the subject of this practical section. In addition to its convenience and accuracy, this tool can be used for a variety of electrical measurements. The steps are as follows:
Step 1: Phase Identification and Proper Positioning
You will need to identify the three phases in the circuit - R (Red), Y (Yellow), and B (Blue). It is important to know the correct order of these phases in order to make accurate measurements. Depending on your estimation of the current level, select the appropriate AC current range on your clamp meter. When in doubt, it's better to start with a higher range.
Step 2: Using the Clamp Meter
The Clamp: Open the clamp up and position it around one of the phases, making sure the jaws fully surround the conductor. For accurate results, make sure the clamp is perpendicular to the conductor.
Caution: Don’t clamp multiple cables at a time. You can only measure current of a single conductor at a time.
Set Measurement Mode: Select the appropriate measurement mode on your clamp meter. If measuring AC current, choose the AC current mode.
Reading the Indicated Current: After repositioning the clamp and setting the mode, gently close the clamp. Through the conductor, the meter will indicate the current flowing.
Step 3: Interpreting the Results
Uniformity in Readings: Ideally, each phase's readings should be the same in a balanced 3-phase system.
Detecting Imbalances: Unbalanced loads or issues within the circuit may appear in readings which show significant variations.
Safety Considerations: Thins you should avoid while measuring 3 phase current
- It is not recommended that you attempt to measure 3-phase current without proper training, since it can pose a safety risk and lead to inaccurate results.
- When dealing with live circuits, never overlook safety measures; always wear the appropriate protective gear and follow safety protocols.
- To avoid erroneous readings and potential equipment damage, make sure all connections are correct.
- You should avoid mixing up phase sequences (R, Y, B) and connection order, which can result in imbalanced circuits and skewed measurements.
- Don't choose a measurement range too low for the current being measured, as this can damage the meter.
- It is important to regularly calibrate your measurement instruments in order to ensure accurate measurements; otherwise, your results may be inaccurate.
- For verification purposes, cross-check readings against known references or alternative methods rather than assuming measurement accuracy.
Final Decision
Hopefully you have understood now how to measure 3-phase current in a circuit. Having worked extensively in the electrical industry, I have experience using both multimeters and clamp meters for measuring 3-phase current.
When it comes to AC measurements, clamp meters are the best because they measure live circuits safely while boasting true RMS accuracy. With its precision, the multimeter shines when it comes to electronic circuits and milliamp measurements. As a result of this knowledge, we can achieve a balance between accuracy, safety, and efficiency when it comes to electrical projects.
FAQs about Measuring 3 phase Current
How is 3 phase voltage and current measured?
Three-phase voltage can be measured with a digital multimeter or a three-phase voltage meter connected across any two phases. To get the actual phase current, a current clamp or current transformer is used around one of the phases, and the obtained value is multiplied by the square root of 3 (1.732).
How is phase current measured?
In order to measure phase current, a clamp or transformer is placed around one of the phase conductors. To determine the actual current, multiply the measured value by the square root of 3 (1.732). This accounts for the phase difference between the phases of the current.
How do you calculate current from 3 phase kVA?
In order to calculate current from 3-phase kVA, use the formula: Current (A) = 1000 x kVA / (sqrt(3) x Voltage (V)). For phase current in amperes, multiply the kVA by 1000 and divide by the product of the square root of 3 and the voltage.
What current is 3 phase?
Current is the flow of electric charge in each phase conductor of a three-phase system. Due to the arrangement of phases, a 3-phase system's total current is typically lower than that of a single-phase system for the same power level.
How do you measure power on a 3 phase supply?
A power meter or a power analyzer designed for 3-phase systems can be used to measure power in a 3-phase supply. By connecting the meter to the system, it will measure the voltage and current in each phase. In order to determine active power (in watts), the meter uses the equation Power (W) = sqrt(3) x Voltage (V) x Current (A) x Power Factor.









