If you were wondering, how does a soldering iron work? Then, read on this post to know it!
Many people ask, how does a soldering iron work? Well, a soldering iron uses a heating element, typically a resistant wire that generates heat when an electric current passes through it.
In 2024, understanding how a soldering iron works involves heating a metal tip, melting solder, which bonds electronic components, ensuring connections in circuits or wires.
The heat is then to transfer to the tip, which melts the solder, it flows and creates a bond between metal surfaces to form a secure connection.
What is a Soldering Iron?
A soldering iron is a hand-held tool used in electronics and electrical work for joining or repairing components. It is specifically for soldering, which involves melting a filler metal, known as solder, to create a permanent bond between two or more metal surfaces.

The soldering iron typically consists of a heat metal tip, usually copper, connect it to an insulate handle. The metal tip is the part that comes into direct contact with the materials being soldered.
Read more aboutHow Long for Soldering iron to Heat Up
How Does a Soldering Iron Work?
Soldering irons are widely present in various applications, including electronics assembly, circuit board repair, wiring connections, and other tasks that involve the joining or modifying of electrical components. Here’s a breakdown of steps to know how does a soldering iron work:
Heating Element
The soldering iron consists of a heating element, usually made of a resistant wire. The heating element reaches high temperatures quickly and maintains a stable temperature throughout the process.
Temperature Control
Many soldering irons feature temperature control mechanisms to adjust the heat output according to the soldering requirements. It is particularly important because different solder alloys have different melting points. The temperature control may be a dial or buttons on the soldering iron handle, allowing users to set the desired temperature.
Tip or Bit
The tip, also known as the bit, is part of the soldering iron directly interacting with the soldered materials. The tip transfers heat from the heating element to the solder joint.
Soldering Stand
A soldering stand is often provided with an iron to hold it securely when not in use. The stand typically has a metal base and a holder or rest to keep the hot soldering iron away from surfaces that could be damaged or cause accidents.
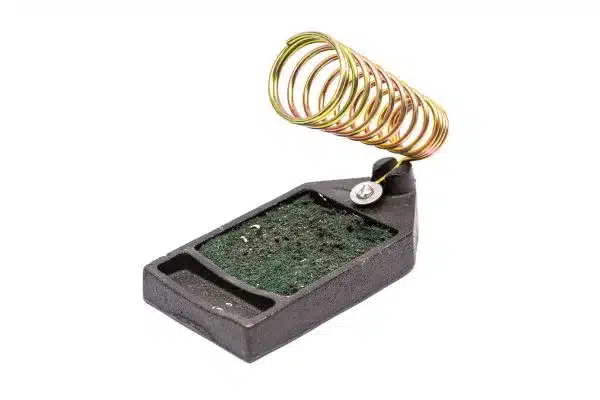

For some soldering stands, a sponge or brass wire cleaner cleans the tip and removes excess solder.
Power Source
Soldering irons can be powered by electricity from an electrical outlet or rechargeable batteries. Electric soldering irons typically have a cord plugging into an electrical socket, while battery-powered ones are portable and offer more freedom of movement.
Read more aboutHow to test computer power supply with multimeter
Soldering Process
To use a soldering iron, follow these steps:
a. Prepare the Joint: Clean surfaces, align components, and secure them.
b. Heat the Iron: Turn on and heat the soldering iron.
c. Apply Solder: Apply solder to the tip, then place it on the joint.
d. Melt and Flow Solder: Touch solder to the joint, allowing it to melt and flow.
e. Remove the Iron: Once the solder flows and bonds, remove the iron, holding the joint until it cools and solidifies.
Safety Precautions
Safety first! Take precautions when using a soldering iron to avoid accidents and injuries. These include using safety goggles or glasses. Additionally, it is crucial to handle the soldering iron with care, especially the hot tip, to avoid burns or electrical shocks.
Remember, soldering irons’ specific features and functionalities may vary depending on the model and manufacturer. Hope so, now you know how does a soldering iron work.
Uses of Soldering Iron
They are must-have tools for professionals and hobbyists with electronics and electrical systems. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of the uses of a soldering iron:
1. Electronics Assembly and Repair
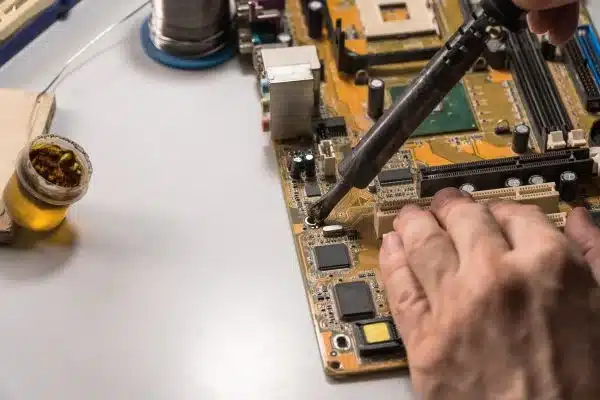

They are instrumental in connecting electronic components to printed circuit boards (PCBs) and creating secure electrical connections. Soldering allows for assembling intricate electronic circuits with precise connections, ensuring proper functionality and reliability.
Read more aboutHow To Repair An Electronic Device?
2. Wiring and Cable Connections
In electrical work, soldering irons are to make wiring and cable connections. They join wires together, creating a permanent and robust electrical connection.
Soldering ensures a low-resistance path for electrical current, preventing loose connections that could cause intermittent or faulty electrical signals. This technique finds common usage in automotive wiring, audio systems, home theater installations, and other electrical applications.
3. Circuit Board Repair
Repairing circuit boards requires indispensable tools like soldering irons. When electronic components become damaged or faulty, they often need replacement. Soldering irons are essential for desoldering defective components by heating and removing the solder joints. Then, new components can be soldered onto the circuit board to restore functionality.
4. Prototype Development
During the prototyping stage of electronic projects, soldering irons are vital tools. They allow designers and engineers to create temporary or permanent connections on breadboards, perfboards, or other prototyping platforms.
Soldering enables them to test and validate circuit designs, make modifications, and iterate on their prototypes. This process is crucial for refining electronic designs and ensuring their functionality before moving on to production.
5. Jewelry Making
Soldering irons find applications in the art of jewelry making. They are used for soldering various metal components, such as wires, clasps, jump rings, and bezels. Soldering allows jewelers to create secure connections and intricate designs in their pieces.
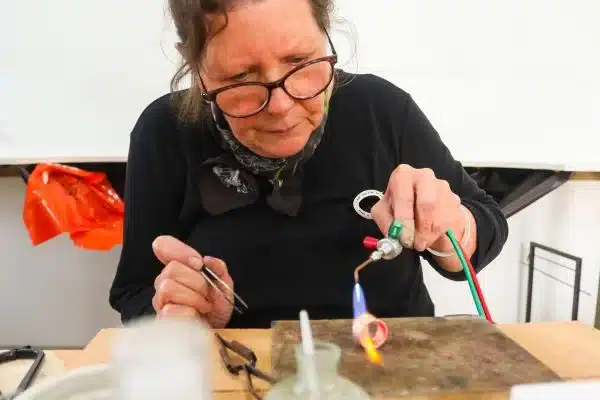

The controlled heat of a soldering iron ensures precise and localized soldering, which is essential for delicate jewelry work. Jewelers often use different types of solder with varying melting points to accommodate different metals and design requirements.
6. Plumbing and Pipe Fittings
Soldering irons are utilized in plumbing to join copper pipes and fittings. The soldering process, known as sweat soldering or sweat fitting, involves heating the joint area of the copper pipes with a soldering iron and applying solder to create a watertight seal.
Soldering provides a reliable and durable connection in plumbing systems and is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing applications.
7. Musical Instrument Repair
Soldering irons play a crucial role in repairing and maintaining musical instruments. Soldering allows technicians to ensure proper electrical conductivity, signal transmission, and functionality of the instrument’s electronic components.
Get creative! Soldering irons are popular for crafts and DIY projects. They enable enthusiasts to create unique electronic projects, build custom circuits, and enhance creativity.
You can use it in creating LED light displays, custom electronic gadgets, robot prototypes, art installations, and other creative endeavors. It provides the means to bring electronic and electrical elements together innovatively.
8. Automotive and Vehicle Electronics
Soldering irons are employed in automotive and vehicle electronics for various purposes. They are used to install and repair vehicle audio systems, including wiring connections and component replacements.
They are also used in automotive electronics repair to fix faulty connections, repair wiring harnesses, and solder circuit board components in engine control units (ECUs), electronic control modules (ECMs), and instrument clusters.
9. DIY Repairs and Home Improvement
Soldering irons can be valuable tools for DIY repairs and home improvement projects. They are useful in fixing broken electronic devices, repairing electrical connections, or soldering wires in appliances, gadgets, or home automation systems.
10. Arts and Crafts
Artists and craftsmen use soldering irons in various arts and crafts projects, especially those that involve stained glass and metalwork. In stained glass work, they utilize soldering irons to join pieces of glass together using solder.
It creates strong and visually appealing connections between glass pieces. Soldering irons allow artists to fuse metal components in metalwork, creating intricate and decorative designs.
11. Model Making and Hobbyist Projects
Model makers and hobbyists frequently use soldering irons for constructing models, miniatures, and dioramas. They are used for soldering electrical components in model train sets, remote-controlled vehicles, aircraft models, and other hobbyist projects.
It allows enthusiasts to create functional electrical systems within their models and bring them to life with lights, motors, and other electronic features.
Tips to Maintain Soldering Iron
To ensure your soldering iron’s longevity and optimal performance, it is important to maintain and care for it properly. Here are some tips to help you maintain your soldering iron:
1. Clean the Tip
Use a damp sponge or brass wire cleaner to gently wipe the tip while it is hot. It helps to maintain good heat transfer and prevent oxidation, ensuring a clean and effective soldering process.
2. Tin the Tip
Tinning the tip refers to applying a thin solder layer to the tip after cleaning. It helps protect the tip from oxidation and maintains its heat conductivity.
Before turning off the soldering iron, melt a small amount of solder onto the tip, ensuring it coats the entire surface evenly. It will help prevent the tip from rusting between uses.
3. Use Soldering Iron Stand
Use a soldering iron stand. It protects surfaces, prevents burns, and keeps the iron stable. Ensure the stand is stable and has a heat-resistant base to avoid accidents.
4. Store Properly
Proper storage is important. Keep your soldering iron safe and dry when not in use for a long time. Ensure that the iron is completely cooled before storing it.
5. Replace Damaged or Worn-out Tips
Over time, soldering iron tips can become worn out or damaged, affecting their performance. It may be time to replace the tip if you notice signs of deterioration, such as pitting, corrosion, or reduced heat transfer.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for replacing tips and ensure you select a compatible tip for your soldering iron model.
6. Avoid Excessive Heat
Using excessive heat for extended periods can cause damage to the soldering iron and its components. It is important to use the appropriate temperature settings for the soldering task.
Avoid unnecessarily high temperatures that could lead to thermal stress, premature wear, or even damage to the soldering iron.
7. Proper Handling
Handle the soldering iron with care to prevent damage. Avoid dropping or mishandling the iron, as it can cause internal damage to the heating element or other components.
8. Regular Calibration and Maintenance
Some soldering irons may require periodic calibration or maintenance per the manufacturer’s instructions. If your soldering iron has replaceable filters, ensure they are cleaned or replaced as needed to prevent clogging and maintain proper airflow.
9. Use Quality Solder and Flux
Using high-quality solder and flux can contribute to the longevity of your soldering iron. Good-quality solder and flux can provide better wetting and flow, resulting in cleaner joints and reducing the chances of residue buildup on the tip.
FAQs
How does a soldering iron create heat?
A soldering iron creates heat through a heating element, typically a resistant wire, which heats up when an electric current passes through it. The heat is transferred to the soldering tip, allowing it to melt the solder and create a bond between metal surfaces.
What is a flux used for?
In soldering, flux facilitates the soldering process by cleaning the surfaces and, removing oxidation and contaminants, and promoting wetting by reducing the surface tension of molten solder. Flux also aids in smooth solder flow, creating strong, reliable connections.
Can I solder without flux?
While it is possible to solder without flux, using flux greatly improves the soldering process. Flux helps clean and prepare the surfaces to be solder, ensuring better wetting and solder flow, resulting in stronger and more reliable joints. It is highly recommended to use flux for optimal soldering results.
What is the difference between solder and flux?
Solder is a metal alloy that creates a permanent bond between two or more metal surfaces when heated. On the other hand, flux helps with soldering. It’s a compound that aids the process. Flux prepares the surfaces by cleaning them and promoting the flow and adhesion of molten solder.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a soldering iron is a versatile tool used for joining or repairing electrical connections, components, and wires. It consists of a heated metal tip, usually made of copper, which melts a filler material called solder to create a conductive bond between two or more surfaces. We hope so; now you know the answer to your question, how does a soldering iron work?
